When testing web applications, it often happens that the testing target does not openly disclose its version information. This makes looking for vulnerabilities a time consuming task, since possibly all versions could be deployed.
Last-Modified
Looking for ways around this issue, I noticed that caching metadata can be of use: Modern web servers often employ a caching mechanism, where JS, CSS or other static files (e.g., images) are served via a cache. This typically results in the "Last-Modified" header being returned, so clients can understand if they need to request a newer version or if their cached version is up to date.

This means, if you want to find the version of a framework, application or anything similar, you should look for a static file path of this software and analyze the Last-Modified response:
Example: Tiki Wiki CMS
With Tiki Wiki I attempted to find the version string via Meta Generator tags,source code comments, ?v GET parameter and half a dozen other techniques without success. Then I noticed that the target page returns a Last-Modified value which is quite old:
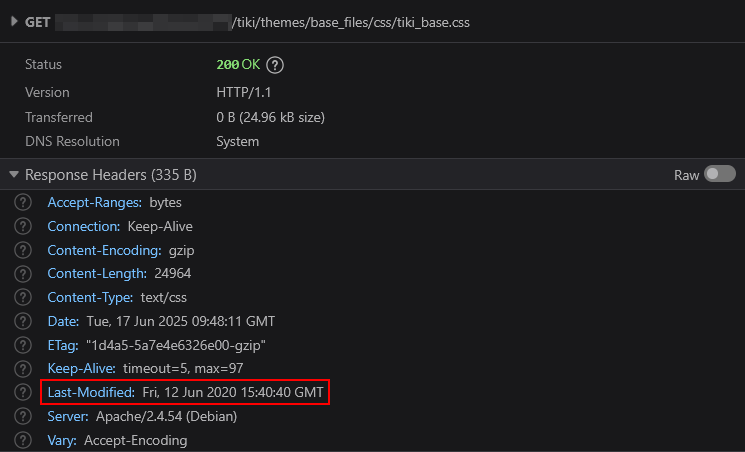
Using the "after:YYYY-MM-DD" directive in Google, I then specifically searched for vulnerabilities and exploits that were released after this deployment date.
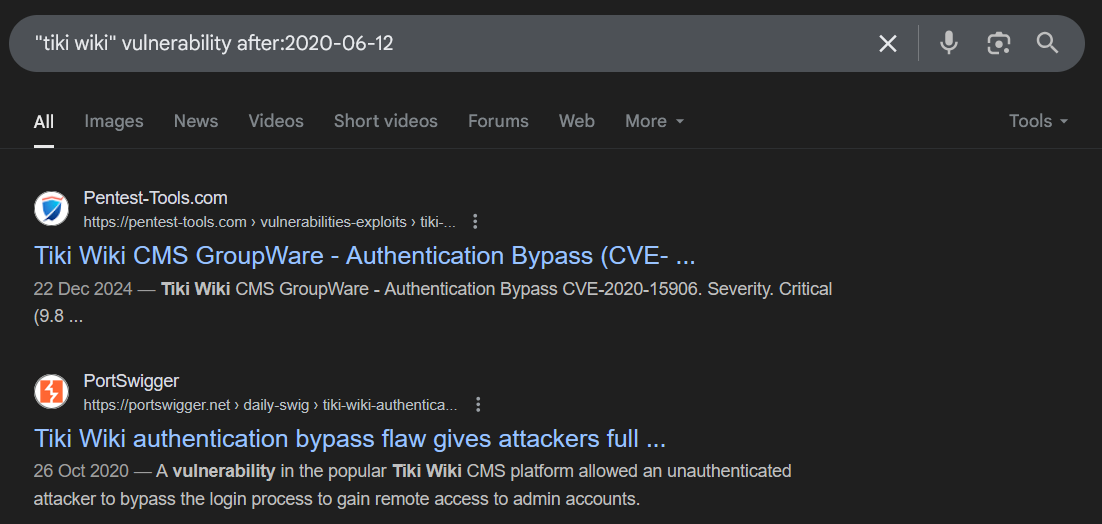
Turns out my target was vulnerable to this exact exploit.
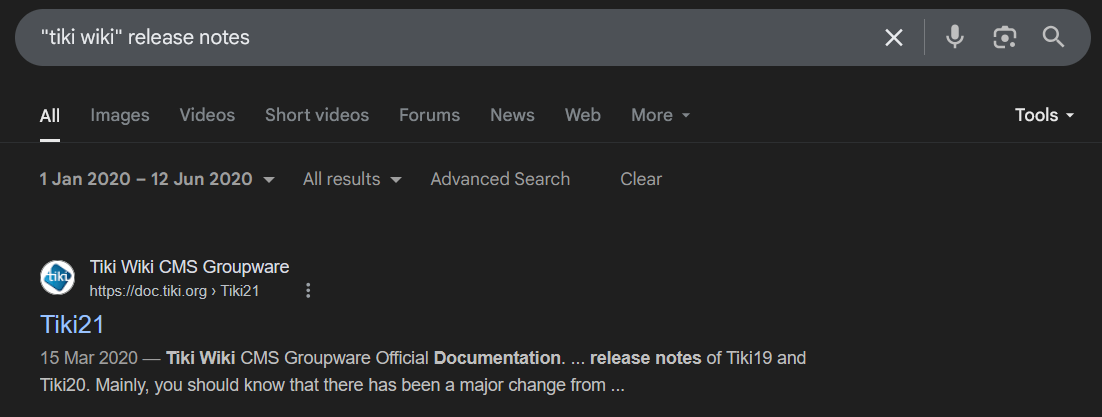
Alternatively, you may use the "custom range" tool to filter the results for release notes and determine an approximate version that fits the Last-Modified date:
Happy hacking ;)
Version Enumeration via Last-Modified Header
Determining exact version strings on a hardened target can be difficult. This post shows how to perform an analysis of Cache metadata to pinpoint the employed software version.
